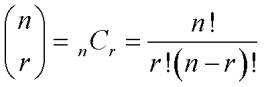Chapter 15
15-1 Presenting Statistical
Data
Frequency distribution: a table that shows how many times each data item occurs.
Histogram: a bar
graph displaying a frequency distribution
Stem and leaf plot: A way of displaying the data in a frequency distribution.
Statistics: the methods used to describe a set of data.
Mode: the number that occurs most frequently
Median: the middle number in a distribution (which must be sorted in order) or the mean of the two middle numbers
Mean: the arithmetic average of the numbers in a deviation of a distribution. The sum of all the data items divided by the number of data items.
15-2 Analyzing statistical
Data Part 1
First quartile: the median of the lower half of the data
Third quartile: the median of the upper half of the data
![]() = The median between
the minimum and the median
= The median between
the minimum and the median
![]() = The median between the median and the maximum
= The median between the median and the maximum
Range = Maximum – Minimum
Box and whisker plot: is used to show the median, the first and third quartiles, and the range of a distribution.
15-2 Analyzing Statistical
Data part 2
Variance: one of the statistics used to measure the dispersion or “spread” of the data.
Standard deviation: the other statistic used to measure the dispersion or “spread” of the data. (The square root of the variance.)
Mean =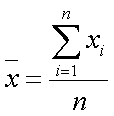
Variance = 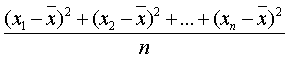
Variance = 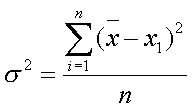
Standard deviation
=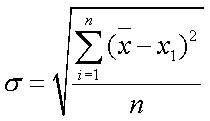
![]()
Statistical Symbols and
Variables:
![]() = The mean of the x values
= The mean of the x values
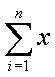 = The sum of the x values
= The sum of the x values
![]() = The variance of the x values
= The variance of the x values
![]() = The number of elements in the distribution
= The number of elements in the distribution
15-5 Fundamental Counting
Principles
Outcome: the result
Event: a subset of outcomes
Compound event: several events which occur together
The Fundamental Counting Principle
In a compound event in which the first event may occur in ![]() ways, the second
event may occur in
ways, the second
event may occur in ![]() ways, etc. The
ways, etc. The
![]() event may occur in
the
event may occur in
the ![]() different ways, so
the total number of ways the compound event may occur is:
different ways, so
the total number of ways the compound event may occur is:
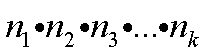
Mutually exclusive choices: you can do one or the other but not both at the same time. The outcome of mutually exclusive choices is the SUM of each outcome.
15-6 Permutations (order, arrange)
Permutation: An arrangement of the elements of a set of definite order.
Ordered Arrangement: A permutation of a set of objects
![]()
![]()
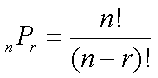
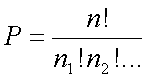 Where objects. n1, n2,
etc., are repeated objects.
Where objects. n1, n2,
etc., are repeated objects.
15-7 Combinations (choose,
select)
The number of combinations of a set of n objects taken r at a time is: