Conic Sections In Standard Form
|
||||
|
|
Circles |
Parabolas |
Ellipses |
Hyperbolas |
|
Horizontal: |
|
|
|
|
|
Equation |
(x-h)² + (y-k)² = r² |
x = a(y-k)² + h |
(x-h)²/a² + (y-k)²/b² = 1 |
(x-h)²/a² - (y-k)²/b² = 1 |
|
Center |
(h, k) |
|
(h, k) |
(h, k) |
|
Axis Of Symmetry |
Any Diameter |
y = k |
See “a” and “b” |
See “a” and “b” |
|
Focus (Foci) |
(h, k) center is focus |
(h+1/(4a), k) |
(h+c, k) & (h-c, k) |
(h+c, k) & (h-c, k) |
|
Directrix |
|
x = h - 1/(4a) |
|
|
|
Vertex (Vertices) |
|
(h, k) |
(h+a, k), (h-a, k), |
(h+a, k), (h-a, k) |
|
Asymptotes |
|
|
|
y= ±(b/a)(x-h)+k |
|
Variables |
r = radius |
|
a = semi-major axis |
a = semi-transverse axis |
|
|
|
|
b = semi-minor axis |
b = semi-conjugate axis |
|
Note: |
|
|
a² > b² |
|
|
"c" is equal to… |
|
|
sqrt ( a²-b² ) |
sqrt (a²+b² ) |
|
Eccentricity: |
e = 0 |
e = 1 |
e = c/a; 0<e<1 |
e = c/a; e>1 |
|
Vertical: |
|
|
|
|
|
Equation |
(x-h)² + (y-k)² = r² |
y = a(x-h)²+k |
(x-h)²/b² + (y-k)²/a² = 1 |
(y-k)²/a² - (x-h)²/b² = 1 |
|
Center |
(h, k) |
|
(h, k) |
(h, k) |
|
Axis Of Symmetry |
Any Diameter |
x = h |
See “a” and “b” |
See “a” and “b” |
|
Focus (Foci) |
(h, k) center is focus |
(h, k+1/(4a)) |
(h, k+c) & (h, k-c) |
(h, k+c) & (h, k-c) |
|
Directrix |
|
y = k - 1/(4a) |
|
|
|
Vertex (Vertices) |
|
(h, k) |
(h+b, k), (h-b, k), |
(h, k + a), (h, k - a) |
|
Asymptotes |
|
|
|
y= ±(a/b)(x-h)+k |
|
Variables |
r = radius |
|
a = semi-major axis |
a = semi- transverse axis |
|
|
|
|
b = semi-minor axis |
b = semi- conjugate axis |
|
Note: |
|
|
a² > b² |
|
|
"c" is equal to… |
|
|
sqrt (a²-b²) |
sqrt (a²+b²) |
|
Eccentricity: |
e = 0 |
e = 1 |
e = c/a;
0<e<1 |
e = c/a; e>1 |
|
For Rectangular
Hyperbolas See the Lecture Notes in your packet or on the Web: |
|
|
http://www.lcusd.net/lchs/dclausen/algebra2/rectangular_hyperbolas.htm |
|
Distance
Formula:
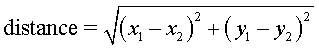
Midpoint
Formula:
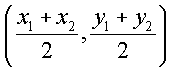
Conic Sections in
General Form: Ax² + By² + Cx + Dy + E =
0
Circles:
For
Circles A = B
A
& B need to have the same number and same sign.
Parabolas:
If
either A = 0 or B = 0 then the equation defines a parabola (x² or y² is
missing). Isolate the variable that is
not squared and use the completing the square method to convert the equation to
that of a Parabola in Standard Form.
Hint:
Solve for y if there is no y² in the equation or solve for x if there is no x²
in the equation.
Ellipses:
1)
A & B have the same sign (both positive or both negative)
2)
A & B are different numbers (if they were the same, this would be a
circle).
Hyperbolas:
1)
A & B must have different signs (one positive and the other negative).
2)
A & B must be different numbers or opposites (same number with different
signs)